- Submissions

Full Text
Aspects in Mining & Mineral Science
Study on Safety and Efficient Production in China Coal Mines
Hu Bingnan*
China Coal Research Institute, Beijing 100013, China
*Corresponding author: Hu Bingnan, China Coal Research Institute, Beijing 100013, China
Submission: December 11, 2020;Published: December 14, 2021

ISSN 2578-0255Volume8 Issue2
Abstract
This paper reviewed the achievement of safety and efficient production in China coal mines. In 2019, the mortality per million tons was 0.083, the mechanization degree of coal mining in large coal mine enterprises reached 96.8%, and the productivity in whole China reached 1000 tons per year per capita. It summarized the main practices on safety and efficiency production in coal mines systematically, especially in scientific and technological progress, intensification layout, policy & regulation, and monitoring & early warning. The paper deeply analyzed main problems on safety and efficient production, such as: management concepts, complex multi-field coupling disasters, unbalanced development, professional talent shortage, and occupational health hazards. At last, the developmental countermeasures were proposed to raise the level of safety and efficiency production in detail.
Keywords: Safety and efficient production; Developmental countermeasures; Complex multi-field; Coupling disasters; Monitoring and early-warning
Outline on Safety and Efficient Production in China Coal Mines
Figure 1: Number of safety and efficient mines in China.
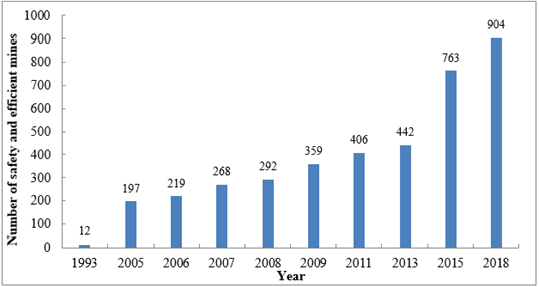
Coal yield was 3.75 billion tons in 2019. It basically reached the balance between supply and consumption. It is expected that coal yield will remain at around 3.6 billion tons in the next decade. In terms of safety, the situation was improved continuously by increasing investment and upgrading technology [1]. The numbers of coal mine accidents and casualties have decreased year by year. In 1978, there were more than 3,000 accidents, more than 4,500 deaths, and the mortality per million tons was 9.436. In contrast, in 2019, there were 170 accidents, 316 deaths, and the mortality per million tons had dropped to 0.083. The coal mine safety level in China has been greatly improved and the results are remarkable. In terms of efficiency, the number of safety and efficient coal mines has increased year by year, from 12 in 1993 to 904 in 2018, shown in Figure 1. There was an obvious rise. The construction of safety and efficient mines raised the overall level, such as: mine design, mine construction, mining equipment, mining technology and management. From 1978 to 2019 in China, the mining mechanization degree in large coal mine enterprises was increased from 32.34% to 96.8% and the per capita productivity in whole China coal mines from 137t per year to 1000t per year [2].
Practices on Safety and Efficient Production in Coal Mines
Technological progress for safety and efficiency development
Unmanned mining technology: A number of major technical
problems which restricting safety production have been solved
by the support of national research plans, and a number of key
equipment in coal mine safety field have been developed, such as:
3D seismic exploration technology with high-resolution, which
can detect a fault with a drop of more than 5m within 1000 m
depth, 8.8m-heigh-seamt mining technology at one time in fully
mechanized mining face, 20m-height-seam (cutting plus caving)
mining technology at one time in fully mechanized caving face, and
so on [3]. In particular, the coal mine intelligence level is greatly
enhanced with the application of advanced network technology.
Taking the automatic control system as the hub and the visual
remote monitoring as the means, the safety and efficient intelligent
mining can be realized in fully mechanized mining face with
“unmanned operation, only someone inspection” during the whole
process of coal mining.
Practice on unmanned mining in Huangling mining group:
Coal seam thickness of test mining face is 1.8 to 2.8m, with an
average of 2.5m. The pseudo-top is mostly mudstone with a
thickness of 0.1 to 0.5 m. Hydraulic support is ZY7800/17/32D,
shearer is MG620/1660-WD, scraper conveyor is SGZ1000/2×855,
transfer machine is SZZ1000/525, and crusher is PLM3000.
The automatic controlling and monitoring system includes the
electro-hydraulic control, industrial Ethernet, working face video
monitor, shearer control and so on. Shearer, hydraulic supports,
transportation equipment, power supply, and liquid supply are all
controlled remotely. One click starts and one click stops. Operation
workers have been reduced from 9 persons to 1 person. It realized
that non-worker for operation and only someone for inspection.
The highest record of eight and a half cuts at one shift was created.
The production capacity can achieve more than 2.0 million tons one
year.
Intensification layout for safety and efficiency development
Intensification mining technology: In order to promote
intensification layout, many large and medium-sized coal mines
have been constructed. A group of world-class coal mines with
more than 10 million tons have been constructed orderly according
to standard of modern coal mines. At the same time, small coal
mines are strictly integrated and closed to eliminate the backward
production capacity. The structure of coal production is adjusted.
Mining layout has been optimized and underground production has
been reasonably centralized to improve coal mining mechanization
degree [4]. The problems with more moves of working face and
low efficiency are solved by reforming mining layout, simplifying
production links, optimizing roadway design, increasing the length
of working face, enhancing mechanized production and automation
control, and improving equipment stability [5]. At the same time, it
creates good conditions for production management.
An example of intensification on production and safety:
CHN Energy Group has built a number of safety and efficient coal
mines by using a series of advanced technology and equipment.
In 2017, it has 64 coal mines with 508.87 million tons yield, the
average yield was 8 million tons, and the mortality per million tons
was 0.005. In the same year, Whole China has 6794 coal mines with
3.52 billion tons yield, the average yield was 0.52 million tons, and
the mortality per million tons was 0.106. Obviously, CHN Energy
Group has higher intensification, higher average yield, and higher
level of safety than whole China. It has become the world leader.
Without considering other factors, the higher the intensification,
the more the safety, there is positive correlation between the two
sides.
Policies and regulations for safety and efficiency development
Policy to resolve excess capacity in coal industry: The State
Council issued No.7 document in 2016, which claimed to quit and
close 500 million tons of coal capacity and to reduce and integrate
500 million tons coal capacity within 3 to 5 years from 2016 [6].
The policy to reduce excess capacity laid the foundation for the
continued improvement of the safety production. Firstly, production
is concentrated in the areas with good resource conditions, and
the proportion of coal production capacity in the areas, including
Shanxi, Shaanxi, Inner Mongolia and Ningxia, is further increased.
Secondly, the productivity level was improved. There are 47
intelligent coal mines, 59 large-scale coal mines with an annual
yield more than 10 million tons, their production capacity nearly
800 million ton yearly. Thirdly, the small coal mines were quitted
and closed at a large intensity, now their production capacity only
accounts for 6.2% of the total production capacity. Fourthly, illegal
production was controlled effectively.
Coal mine safety regulations: Coal Mine Safety Regulations
was revised and implemented since Oct.1, 2016. The new regulation
strongly encourages coal mines to adopt new technology and
improve the level of production and safety. The overall effect was
good since the implementation of the new regulation. The mortality
per million tons had dropped nearly 50% in 2018, compared with
that in 2016.
Special action to reduce underground workers: Special action
of thousand- people-scale mine was organized by China government
in 2016. Seven expert groups were organized to investigate in 48 coal mines to compile the technical countermeasures for each
mine to reduce people. Through this action, at the end of 2018,
the maximum number decreased below thousand people in the
single shift underground in 48 coal mines. This action promoted
the progress of safe and efficient work. Taking Shanxi Province as
an example, the number of deaths in coal mines in 2018 decreased
53.13%, the mortality per million tons is 0.033 which approaching
the 0.01 in developed countries. Also, there is no major accident,
thus the safety level was greatly improved.
The aim of special action is to reduce underground worker
number in single shift below 1000 people. It was organized by
China government in 2016. Seven expert groups were organized
to investigate the conditions in 48 coal mines and compile the
technical countermeasures for each mine to reduce workers. At the
end of 2018, underground worker number in single shift decreased
below 1000 people in all mines. This action promoted the progress
of safety. Taking Shanxi Province as an example, the number of
deaths in coal mines in 2018 decreased 53.13%, the mortality per
million tons is 0.033 which approaching the 0.01 in developed
countries. Also, there is no major accident, thus the safety level was
greatly improved.
Monitoring, early-warning and emergency rescue for safety production
Disaster monitoring and early-warning technology:
National Science and Technology Development Plan (2006-2020)
add the early-warning and emergency rescue of major production
accidents into the public safety field. It is good for breaking
through key technologies, developing new emergency rescue
equipment, strengthening technology integration application
and industrialization demonstration, such as detection and
identification technology of disaster hazard source, intelligent
monitoring technology and equipment for dynamic evolution of
disasters, self-analysis and early-warning evaluation model for
major disasters based on big data.
Emergency rescue system: The State Council issued No.99
document in 2013, which claimed to raise the scientific level
of emergency rescue and strengthen the construction of coal
mine emergency rescue equipment. Based on the large coal
industry groups, 7 national emergency rescue teams (bases), 17
regional teams and 45 central enterprises rescue teams has been
constructed. Based on the mining production companies, part-time
emergency rescue team has been constructed. The technology and
equipment are developed, such as detection and positioning of
workers in disaster areas, rapid drilling of emergency life channel.
The emergency rescue management and plan system are basically
formed. The emergency rescue scale of team and equipment has
been gradually expanded.
Problems on Safety and Efficient Production in Coal Mines
Problems of management concepts
Although good results with four decline items were achieved in China’s coal mines in 2018, including total accidents, large accidents, heavy accidents, and the mortality per million tons. But there is still a big gap when compared with international advanced level of mortality per million tons of 0.01. There still exist many management problems in coal mines, such as: short of fine management, weak awareness in disasters prevention, insufficient understanding in regional prevention for compound disasters, lack of the concern for occupational health hazards besides control of casualty. Compared with the goal of good life in new era, it is necessary to change the management concepts to meet the need of safety and efficient production in China coal mines.
Problems of complex dynamic disasters
The coal mine disasters have becoming more and more serious in deep mining in east China [7,8]. The mining depth is increased 10-20m per year in coal mines. There are 50 coal mines with mining depth more than 1000m in China, in which the maximum mining depth is 1500m and the maximum ground stress more than 40MPa. There are 62 coal mines with high temperature, in which there are 38 coal mines with the temperature more than 30 ℃ in working faces. Because of deep mining, gas problems are more severe. In mining area of western China, dynamic disasters are prominent with increasing mining intensity in extra-thickness coal seam. Disaster probability of high ground pressure, high geothermal temperature, high gas, rock burst, and their compound, is getting bigger. Geological disasters are transformed from singletype to coupled-type, which more difficult to prevent from. Due to the characteristics of complex coupled dynamic disasters with suddenness, strong impact, it is difficult to solve the disasters only by local partial measures.
Problems of unbalanced development
From the view of region, the construction of safety and efficient coal mines has been highly valued in Shanxi, Henan, Shandong and Hebei province. The relevant planning and policy were formulated by the local governments. They have achieved remarkable results. But in Southwest and South China, due to poor geological conditions and difficult mining conditions, the degree of mining mechanization is generally low, and the indexes in the areas are far away from the standards of safety and efficient mines [9,10]. From the view of structure, there are still 2000 small coal mines in China, accounting for about 28% of the total coal production. From the view of equipment, mining technology in some coal mine is still backward and the mechanization level is low. From the view of disaster type, there is an upward trend in rock burst accidents.
Problems of professional talent shortage
96% coal mines are short of mechanical and electrical professional talents and 88% coal mines are short of mining professional talents in China. Few graduates pay attention to the coal enterprises. It is extremely difficult to recruit professional talents in recent years. Coal enterprises are not attractive because of hard work, living environment, and relatively low welfare benefits. The tendency of de-coal in coal-related colleges is becoming more and more obvious. From the view of employment, the graduate employment rate in geology and mining major is about 90%. Data of admission and employment in coal mines in China University of Mining and Technology (CUMT) and Heilongjiang University of Science and Technology (HUST) are shown at table1.Taking HUST as an example, 44.67% of graduates were engaged in their related majors in coal mines in 2013. Since 2014, the employment rate has been declining quickly. Only 6.34% of the graduates were engaged in those related majors. Due to few graduates go to work in coal mines and old professional talents retired with the age, the professional talent shortage has limited the promotion and application of advanced technical equipment in coal mines.
Problems of occupational health hazards
According to statistics from 26 coal enterprises, the new added pneumoconiosis patients is 8300 and the deaths is nearly 1500 people in 2013. Compared with data in 2005, they increased 85.39% and 118.97%, respectively. According to the statistical bulletin in 2017, the occupational pneumoconiosis patients are total 22,701, in which there are about 11,000 in coal mines. Occupational health hazards are becoming more and more prominent in coal mines.
Countermeasures to Improve Safety and Efficient Production in Coal Mines
Changing outdated concepts on safety and efficient production
In order to improve safety production level in coal mines, it is necessary to implement four changes from outdated concepts of safety production. The first is the change from control of disaster accidents to prevention of disaster source. The second is the change from the single disaster prevention to the multi-disaster prevention. The third is the change from partial governance to regional governance. And the fourth is the change from control of the death to guarantee of the health. As a result, we reach disaster prevention and control in the whole process of coal mining (premining, during mining and post-mining); reach precise intelligent mining, precise disaster prevention and precise treatment, and makes the coal industry become a high-tech industry with high safety level and harmless.Strengthening scientific & technological research and demonstration
Government gives full play to the enthusiasm of multi-parties
(industry-college-institute) to boost the science & technology
innovation. Multi-parties should be focus on research of key
technology and subversive theory to reduce mine disasters in
essence, develop the prevention and control technology of dynamic
multi-field coupling disasters, to develop the remote controllable
unmanned precision mining technology and equipment, and
compile the design specifications, the construction standards and
the mining regulations that meet the requirements for safety and
efficiency.
Taking safety mining and efficient mining as two main lines,
the transformation of advanced scientific and technological
achievements should be accelerated. The new mode of integrated
mining and disaster prevention should be created. Demonstration
projects with information, digitization and intelligence which cover
integrated production, disaster monitoring, and prevention &
control management.
Improving the overall level of safety and efficient production
For new coal mine, it should be built at a high starting point, which meet large-scale modernization and safety & efficient mine standards. For old large and medium-sized coal mine, it should improve the degree of mechanization by technological transformation. For coal enterprise, it should increase the industrial concentration by merging coal enterprises and integrating coal resource so as to eliminate backward production capacity gradually. For whole China, we should exchange and share the experience in technology, engineering, and management on the construction of safety and efficient mine timely. The aims are to solve the problem of imbalance and inadequacy and to promote the overall level in safety and efficient development.
Strongly training professional talents
It is necessary to strengthen the main channel function of personnel training in universities to provide sufficient graduate source for coal enterprises; to train young and middle-aged professional talents in coal mines by updating their knowledge and exchanging technological achievements regularly. The qualification of workers in coal mines should be supported to certificate, according to the national occupational skills standards. At the same time, the qualification allowance should be provided fully. Their wage should be increased to improve living conditions. A long-term plan should be established to attract professional talents to work in coal mines. As a result, a group of compound professional talents who master safety technology, understand safety management and be able to operate on-site should be trained to meet the needs of mechanization, automation, information, intelligence in coal mines. It solves the problem of professional talent shortage completely.
Building a better occupational health system
It should establish a unified third-party online testing center for real-time supervision and early-warning of underground respiratory dust hazard by learning from developed countries such as the United States and Germany. It should formulate the limit of dust concentration of underground environment, limit of work time, and the regulations of individual protection according to the standard that workers have no pneumoconiosis after underground working for 25 years. It should put the occupational health into the safety assessment system of companies and local governments so as to further control the deterioration trend of occupational health in coal mines.
Acknowledgment
The paper was financially supported by National Science and Technology Major Project : 2016ZX05068002003.
References
- Liang Y (2017) Strategic studies of high-efficient and energy-effective coal extractions in China. Science Press, Beijing, China.
- Hu BN, Zhang P (2016) Research on development environment of safety and efficient mine construction of China during 13th five-year period. Coal Economic Research 36(11): 11-16.
- Wang GF, Fan JD, Xu YJ (2018) Innovation progress and prospect on key technologies of intelligent coal mining. Industry and Mine Automation 44(2): 5-12.
- Zhang JG, Wang H (2018) Practice of safety and efficient production with less personnel boosted by four optimizations and one promotion for coal enterprise and its inspiration. China Energy and Environmental Protection 40(7): 1-4.
- Ning Y (2011) Innovating safety and high-efficiency coal mining technology and supporting extra-large mine construction. Coal Mining Technology 16(3): 1-3.
- Qin RJ (2019) Research on current status and policy of coal mining in China. Coal Economic Research 39(1): 57-61.
- Lan H, Chen DK, Mao DB (2016) Current status of deep mining and disaster prevention in China. Coal Science and Technology 44(1): 39-46.
- Li Wanming (2013) Review of the current situation of safety and efficient mining in mines in China. Science and Technology Innovation Heraid 20: 112.
- Shen BH, Guo YH (2012) Development status and tendency of technology and equipment for fully mechanized coal mining in China. Coal Science and Technology 40(2): 1-3.
- Wu J (2016) Innovative management and control mode to promote safety and efficient mine construction. China Coal Industry 6: 49-51.
© 2021 Srivatsan TS. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






