- Submissions

Full Text
Annals of Chemical Science Research
Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicle Application
Venkata Sai A1,2, Vincent M1,2 and Vinod Kumar E1*
1IMDEA Materials Institute, Spain
2Faculty of Science, Autonomous University of Madrid, Spain
*Corresponding author: Vinod Kumar E, IMDEA Materials Institute, Spain
Submission: June 15, 2020Published: June 23, 2020

Volume2 Issue2June, 2020
Introduction
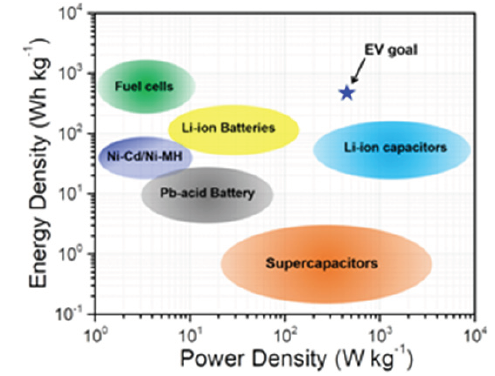
Development of advanced renewable energy storage systems is crucially important to combat the increased usage of fossil fuels. Secondary batteries are superior to other energy storage technologies due to their high energy density and conversion efficiencies (Figure 1). In recent years, secondary lithium-ion batteries become an integrated part of our life due to its widespread use in consumer electronics, medical devices and electric vehicles [1]. However, implementation of current generation lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) in commercial electric vehicles are limited by their low energy density (100-250Wh kg-1) and power density (250-400W kg-1) [2]. Pack level energy density exceeding 350Wh kg-1 is necessary for electric vehicles with a driving range of 500km [3]. In this regard, many approaches are being pursued to improve the electrochemical performance of Li-ion battery electrochemistry with the use of high-performance nanostructured electrode materials.
Figure 1: Ragone plot of different energy storage devices.
Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles
Electrode materials for state-of-the-art automotive Li-ion batteries have to meet several requirements including high specific capacity, long cycle-life, good mechanical and chemical stability over a wide temperature range and safe operation [4]. Conventional Li-ion batteries usually consist of graphite /Li4Ti5O12 anodes and LiCoO2/LiFePO4 cathodes. Storage capacities and safety characteristics of these batteries are inadequate for application in electric vehicles [3,5]. Although different cell components including electrolyte solutions, electrode-electrolyte interfaces and separators are important, physio-chemical properties of electrode materials are the key factor deciding Li-ion storage performance. Hence, immense efforts have been focused on the development of advanced high capacity alloying/conversion anodes and high voltage LiMO2 cathodes (where M is a combination of Ni, Co, Al/Mn). One of the most widely used strategies to improve the electrochemical performance is the fabrication of nanostructured electrodes [6]. Another approach is the hybridization of active material with carbonaceous substrates such as graphene, carbon nanotubes and carbon fibres. Nevertheless, development of high-performance Li-ion batteries for long range electric vehicles remains as a challenge.
Pseudocapacitive Li-ion storage has been recently investigated as a strategy to significantly improve the Li-ion storage performance [7]. This process usually involves surface/near surface diffusion independent charge storage facilitated by defects and interfaces. Pseudo-capacitance of metal oxide anodes such as TiO2, V2O5, Nb2O5, TiNb2O7 and Li4Ti5O12 are investigated recently [8-11]. Ultralong cycling stabilities and high-power densities and can be obtained for pseudocapacitive electrodes due to the minimum structural changes and diffusion independent Li-ion intercalation, respectively. Moreover, synergy between conventional Li-ion intercalation and unconventional pseudocapacitive surface Li-ion storage often result in high energy densities that are difficult to achieve otherwise. Nevertheless, energy density of these intercalation type electrodes are low and pseudocapacitive Li-ion storage is minimal in the case of conversion and alloying type high capacity anodes. Extrinsic pseudo-capacitance, which can be induced through nano-structuring, remains elusive in the case of conversion and alloying type anodes. Li-ion storage of metal oxide and phosphate-based cathodes also follow a diffusion limited intercalation mechanism. Pseudocapacitive and double layer type Li-ion storage is also negligible in these cathodes due to their low surface area and large particle size. It is therefore necessary to induce pseudocapacitive Li-ion storage in high capacity electrodes to further enhance energy/power density and cycling stability.
Engineering of electrode materials containing defects (anion/cation vacancies, dislocations, grain boundaries etc.) and interfaces (metal oxide-metal oxide, metal-metal oxide, metal oxide-carbon etc.) are key to induce pseudocapacitive type Li-ion storage in Li-ion battery electrodes, and more research is necessary in this direction. In conclusion, diffusion limitation of Li-ions and single type ion storage mechanism is one of the crucial factors limiting the performance of current generation Li-ion batteries. In our opinion, electrode materials that can store Li-ions through multiple mechanisms are key for the development of high energy and power density Li-ion batteries with excellent cycling life and safety characteristics. Designing of such environmentally friendly electrode materials and their large-scale production is also important for the real-world implementation of high-performance Li-ion batteries for electric vehicle application.
Conclusion
Despite of the numerous advances in the area of electrochemical energy storage, development of high-performance Li-ion batteries for long-range electric vehicles remains as a challenge. While research on alternate battery technologies based on Na, Mg, Ca, K and Al ions are at early stage, Li-ion batteries are still the most versatile technology suitable for electric vehicle market. Consequently, development of high energy/power density and long-life Li-ion batteries has been the subject of intense research. Although electrolyte compositions and electrode-electrolyte interfaces affect the battery performance, electrode materials depending on single type of diffusion-limited ion storage is the key factor responsible for the mediocre performance of Li-ion batteries. In our opinion, defect and interface engineered electrode materials that can store Li-ions through multiple mechanisms are crucial for the development of advanced Li-ion batteries for implementation in long-range electric vehicles.
References
- Goodenough JB, Kim Y (2010) Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries. Chem Mater 22(3): 587-603.
- Etacheri V, Marom R, Elazari R, Salitra G, Aurbach D (2011) Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review. Energy Environ Sci 4(9): 3243-3262.
- Liu J, Bao Z, Cui Y, Dufek EJ, Goodenough JB, et al. (2019) Pathways for practical high-energy long-cycling lithium metal batteries. Nat Energy 4: 180-186.
- Schmuch, R, Wagner R, Hörpel G, Placke T, Winter M (2018) Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries. Nat Energy 3: 267-278.
- Zeng X, Li M, El-Hady DA, Alshitari W, Al-Bogami AS, et al. (2019) (2019) Commercialization of Lithium Battery Technologies for Electric Vehicles. Adv. Energy Mater (2019) 9, 1900161.
- Aricò AS, Bruce P, Scrosati B, Tarascon JM, Schalkwijk WV (2005) Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices. Nat Mater 4(5): 366-377.
- Augustyn V, Simon P, Dunn B (2014) Pseudocapacitive oxide materials for high-rate electrochemical energy storage. Energy Environ Sci 7: 1597-1614.
- Augustyn V, Come J, Lowe MA, Kim J, Taberna PL, et al. (2013) High-rate electrochemical energy storage through Li+ intercalation pseudo-capacitance. Nat Mater 12(6): 518-522.
- Lübke M, Shin J, Marchand P, Brett D, Shearing P, et al. (2015) Highly pseudocapacitive Nb-doped TiO2 high power anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3: 22908-22914.
- Xiang Y, Yang Z, Wang S, Hossain MSA, Yu J, et al. (2018) Pseudocapacitive behavior of the Fe2O3 anode and its contribution to high reversible capacity in lithium ion batteries. Nanoscale 10(37): 18010-18018.
- Yu X, Yun S, Yeon JS, Bhattacharya P, Wang L, et al. (2018) Emergent pseudo-capacitance of 2D nanomaterials. Adv Energy Mater 8(13): 1702930.
© 2020 Vinod Kumar E. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






