- Submissions

Full Text
Advances in Complementary &Alternative Medicine
Endorphins-A Forgotten Hidden Magic Holistic Healer: Mini Review
Shrihari TG*
Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Oncology, Krishnadevaraya College of Dental Sciences, India
*Corresponding author: Shrihari TG, Assistant professor, Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Oncology, Krishnadevaraya College of Dental Sciences, Bengaluru-562157, India, Email: drshrihariomr@gmail.com
Submission: April 24, 2018;Published: May 10, 2018

ISSN: 2637-7802Volume2 Issue5
Abstract
Aim: Endorphins are endogenous morphine, neuropeptide, produced from pituitary gland in response to stress and pain. There are three types of endorphins are beta-endorphins, dynorphins, enkephalins binds to mu, kappa, delta receptors found on immune cells and nervous system. Betaendorphins is a most abundant endorphins synthesized and stored in the anterior pituitary gland.
Material and methods: To search and find out about endorphins and their mechanism of action in treatment of diseases such as cancer, autoimmune diseases and infectious diseases.
Results: It has got various activities such as immune stimulatory, anti-inflammatory, analgesic activity, delay aging, stress buster activity involved in preventive, promotive, therapeutic and palliative treatment of various diseases such as cancer, auto-immune diseases, infectious diseases.
Conclusion: Endorphins especially beta- endorphins involved in preventive, promotive, therapeutic and palliative, holistic treatment of various diseases such as cancer, auto-immune diseases, infectious diseases, without adverse effects and inexpensive.
Keywords: Cortisol; HPA-axis; P53; NF-KB; STAT-3; Noradrenaline
Abbreviations: IL-1: Interleukin 1; IL-2: Interleukin 2; IL-6: Interleukin 6; IL-12: Interleukin-12; TNF-oe: Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha: NF-kB: Nuclear Factor-kappa B receptor; STAT-3: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-3; Th1: Type 1 helper cells; Th2: Type 2 helper cells; mmp-2,9: matrix-metallo proteases 2,9; Tregs: Regulatory T cells; IL-18: Interleukin 18; IFN-γ: Interferon Gamma; IL-10: Interleukin 10; CRH: Corticotrophic Releasing Hormone; HPA-Axis-Hypothalamo Pituitary Adrenal Axis
Introduction
Endorphins are endogenous morphine, neuropeptides, synthesized in pituitary gland in response to stress and pain mediated release of CRH (Corticotropic releasing hormone) from hypothalamus activate the release of neuropeptides such as ACTH (Adreno corticotropic hormone), cortisol and noradrenaline. These neuropeptides activate inflammatory mediators such as IL- 1β, TNF-α, IL-6 and COX-2 inflammatory mediators activate key transcription factors such as NF-kB, STAT-3, involved in tumor progression, chronic inflammation, immune modulation leads to auto immunity [1-3].
Material and Methods
Endorphins are of three types such as beta- endorphins, enkephalins, dynorphins binds to mu, kappa, and delta receptors respectively. Beta-endorphins are the most abundant, potent endorphins, synthesized and stored in the anterior pituitary gland is a precursor of POMC (Pro-opiomelanocortin). Beta-endorphins is an abundant endorphins produced in response to stress and pain, release CRH from hypothalamus activates HPA-axis through ANS results in release of ACTH, cortisol, and noradrenaline neuropeptides which activates IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6 pro-inflammatory cytokines and COX-2 inflammatory mediator which inturn, activates NF-KB, STAT-3 transcription factors involved in tumor progression by cell proliferation, angiogenesis, cell survival, invasion and metastasis. Beta-endorphins has got various activities such as immunestimulatory, anti-inflammatory, analgesic activity, delay aging, stress buster activity, involved in preventive, promotive, therapeutic and palliative, holistic treatment of various diseases such as cancer, auto-immune diseases, infectious diseases.
Discussion
Receptors of endorphins are increased during stressfull conditions located on nervous system and immune cells. Receptors of endorphins on peripheral nerves are increased during stressfull conditions. Most of all immune cells produce endorphins. In inflammatory condition recruitment of immune cells to the site of inflammation by chemokines produce endorphins, acts as anti-inflammatory activity by production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-18, IL-10 and IFN-gamma. Endorphins decreases the activity of sympathetic nervous system, thereby decreasing inflammatory mediators IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6 and COX- 2. It inhibits neuropeptides such as cortisol and noradrenaline mediated activation of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1, TNF- α, IL-6, which inturn activates transcription factors NF-KB and STAT-3 involved in tumor progression. Endorphins has an activity of immune stimulatory, endorphins binds on the receptors situated on immune cells such as NK cells, macrophages, T cells and B cells produce IFN-gamma, opsonin, granzyme-B, antibodies, acts as antitumor, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activity [4-8].
In the PNS, binding of endorphins to the receptors on peripheral nerves results in inhibition of substance P, a neurotransmitter of pain and inflammation, results in analgesia and reduce inflammation. In the CNS, binding of endorphins to the receptors present in CNS results in inhibition of GABA inhibitory neurotransmitter, activation of dopamine neurotransmitter responsible for euphoria, tranquility of mind, stress buster activity and analgesic activity. Beta-endorphins suppress NF-KB, which involves in auto-immune diseases by conversion of TH1 to TH2 lymphocytic type, TH17 cells, alteration in Tregs, which otherwise involved in immune homeostasis and self tolerance, results in immune modulation, cellular changes, tissue damage by matrix mettaloproteases, leads to auto-immune disease [9-20] (Figure 1). Beta-endorphins inhibits aging by reducing free radicals release during oxidative burst from inflammatory cells such as tumor associated macrophages, tumor associated neutrophils, dendritic cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, TNF-α, IL-8 and other mechanism is by lengethening telomeres, which otherwise shortens with aging [21- 25].
Figure 1: Mechanism of action of beta-endorphins.
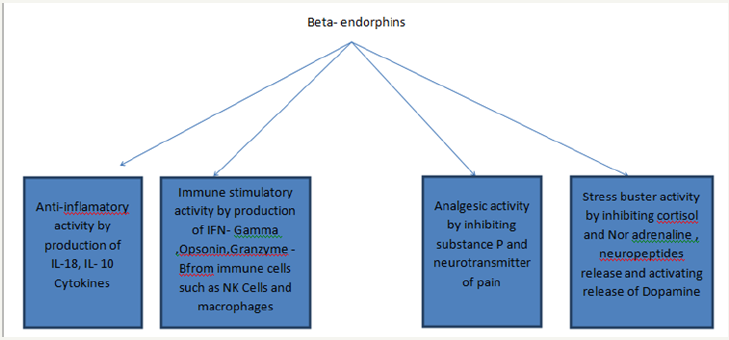
Beta-endorphins involved in inhibiting alteration of P53 tumor suppressor gene and its expression in tumor microenvironment by suppressing the antagonistic effect of NF-KB on P53. Suppressing the inflammatory mediators such as free radicals (ROS, RNS) and NO released from tumor associated macrophages, tumor associated neutrophils, DCs involved in mutation of P53 in inflammatory tumor microenvironment and tumor progression. Beta- endorphins increase E-cadherin expression in epithelial cells, which helps in cell adhesion. Loss of E-cadherin involved in epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced tumor invasion [4-10,21-23].
Factors Responsible for Release of Endorphins
Meditation, pranayama, intense physical exercise, acupuncture, Love, care, music therapy release endorphins. Vigorous physical activity release endorphins creates psychological relaxed state known as runner’s high due to release of dopamine neurotransmitter involved in self reward, euphoria, cognition and addiction. Endorphins are produced in our body in response to stress and pain acts as a holistic preventive, promotive, therapeutic and palliative treatment of choice in autoimmune diseases, cancer, infectious diseases, without adverse effects and inexpensive.
Comments
A. Activities that produce endorphins.
B. Quantity of endorphins produces during activities.
C. Duration of various effects by endorphins need to be known.
D. Mechanism of actions of different types of endorphins.
E. Thorough understanding of mechanism of action on different diseases related to prognosis.
Conclusion and Future Perspective
Endorphins are neuropeptide’s produced from pituitary gland in response to pain and stress release CRH (corticotrophic releasing hormone) from hypothalamus activate HPA axis (hypothalamo pituitary adrenal axis) release cortisol and nor-adrenaline mediated activation of inflammatory mediators IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6 from inflammatory cells activate NF-KB, STAT-3 transcription factors involved in tumor progression, auto-immune diseases, infectious diseases. Beta-endorphins is an abundant endorphin synthesized and stored in pituitary gland involved in immune stimulatory, anti-inflammatory, stress buster, analgesic activity in treatment of various diseases. It acts as a future preventive, promotive, therapeutic and palliative treatment of diseases and dose dependent action on prognosis of disease need to be known.
References
- Shrihari TG (2017) Quantum healing approach to new generation of holistic healing. Transl Med 7(3): 198.
- Archana S, Deepali V (2014) Endorphins: Endogenous opioid in human cells. World journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences 4(1): 357- 374.
- Zhang, Chang Q (2013) Role of Beta-endorphin in control of stress and cancer progression in fetal alcohol exposed rats. Thesis.
- Shrihari TG (2017) Endorphins on cancer: A novel therapeutic approach. J carcinog Mutagen 8: 298.
- Lennon FE, Moss J, Singleton PA (2012) The μ-opioid receptor in cancer progression: Is there a direct effect? Anesthesiology 116(4): 940-945.
- Nuamtanung Y, Vorapongpiboon S, Thongpan A, Boonyaprasit S (2005) Effects of meditation on the T-lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, NK cells production. KasetsartJ (Nat Sci) 39: 660-665.
- Michael FJ, Elizabeth OS, Nikola LV, Wenhui L (2011) Acupuncture may stimulate anticancer immunity via activation of natural killer cells. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 6(4): 1-14.
- Arora S, BhattacharJee J (2008) Modulation of immune responses in stress by yoga. Int J Yoga 1(2): 45-55.
- Jonsdottir IH (2000) Special feature for the olymphics: Effects of exercise on the immune system: Neuropeptides and their interaction with exercise and immune function. Immunol Cell Biol 78(5): 562-570.
- Jose RI, Fernando P, Juan IR, Justo S, Maria LD, et al. (2014) Levels of immune cells in transcendental meditation practitioners. Int J Yoga 7(2): 147-151.
- Naghmeh HA, Michael M, Amita KH, Nicholas SP, Peter JC (2014) Front biotransformation of beta-endorphin and possible therapeutic-frontiers. Pharmacol 19(1): 1-8.
- Saba GC (2011) The immune-endocrinal system: Hormones, receptors and endocrine function of immune cells-The packed transport theory. Advances in neuroimmune biology 1(1): 71-85.
- Bardt J, Dileo C, Grocke D, Magill L (2011) Music interventions for improving psychological and physical outcomes in cancer patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 8: CD006911.
- Kiecolt GJK, Bennet JM, Andridge R, Peng J, Shapiro CL, et al. (2014) Yoga’s impact on inflammation, mood, and fatigue in breast cancer survivors; A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol 32(10): 1040-1049.
- Nani M, Irwin MR, Chung M, Wang C (2014) The effect of mind-body therapies on the immune system-Meta analysis. PLos One 9(7): 10-24.
- Priyadarshini S, Palok A (2012) Effects of psychological stress on innate immunity and metabolism in humans: A systematic analysis. Plos One 7(9): 8-15.
- Adam SPB, Smith G, Sugai d, Parsa FD (2010) Understanding endorphins and their importance in pain management. Hawaii Med J 69(3): 70-71.
- Fancourt D, Ockelford A, Belai A (2014) The psychoneuroimmunological effects of music: A systematic review and a new model. Brain Behav Immun 36: 15-26.
- Sedlmeir P, Eberth J, Schwar ZM, Zimmermann D, Haarig F, et al. (2012) The psychological effects of meditations: A meta-analysis. Psychol Bull 138(6): 1139-1171.
- Dipak KS, Sengottuvelan M, Changqing Z, Nadka B (2012) Regulation of cancer progression by Beta-endorphin neuron. Cancer Res 72(4): 836- 840.
- Zhang C, Murugan S, Boyadjieva N, Jabbar S, Shrivastava P, et al. (2015) Beta endorphin cell therapy for cancer prevention. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 8(1): 56-67.
- Shrihari TG (2017) Dual role of inflammatory mediators in cancer. Ecancermedicine 11: 721-730.
- Shrihari TG (2017) Quantum healing-A novel current concept of holistic healing. International Journal of Complementary and Alternative Medicine 10(2): 329.
- Ljudmila S (2010) Stress and autoimmunity. Autoimmunity Reviews 9(5): A271-A276.
- Stojanovich L, Marisavijevich D (2008) Stress as a trigger of autoimmune disease. Autoimmun Rev 7(3): 209-213.
© 2018 Shrihari TG. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)














.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)










.jpg)






.png)

.png)



.png)






