- Submissions

Full Text
Modern Research in Dentistry
Awareness of Dentist about Common Diseases and their Lab Investigations
Magdy Khaled Hamam*, Abdulmalek Yahya Alyahya, Salman Zaid Alotibi and Abdulaziz Abdullah Alqahtani
Head Division of Oral Medicine, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia
*Corresponding author:Magdy Khaled Hamam, Professor, Head Division of Oral Medicine, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia
Submission: May 09, 2018;Published: August 10, 2018

ISSN:2637-7764Volume3 Issue2
Abstract
The purpose of the research increases the awareness of dentist about common diseases and their tests and to know the normal value for each test. Prospective study Survey containing multiple choice questions and checklist to know the level of knowledge of dentist and dental student it was digital survey estimation of sample size 120 participants and collected and analyzed statistically. Five questions above 80% and average of 71% for all questions. The results showed least awareness in the answers was the answers of questions 6 and 14. (Q6. what is/are the tests used to measure blood pressure?) And correct answer was sphygmomanometer and Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and 47.1% of participants answered it correctly. (Q14. what is the normal Thrombin Time?) The correct answer was between 9 to 13 seconds and 28.9% of participants answered it correctly. In the other hands the highest awareness in the answers was the answers of questions 7,8 and 12. (Q7. what is the normal Platelet Count?) The correct answer was 150,000 to 450,000/mm3 and 86.6% of participants answered it correctly. (Q8. what is the normal Bleeding Time?) The correct answer was Between 1 to 6 minutes and 90.1% of participants answered it correctly. The education level factor in the group statistic showed the highest mean were general practitioner and consultants due to the knowledge and the experience while dental interns and dental students showed the lowest mean because the dental student lack the knowledge. There is awareness in the dentists and dental students because the average of the correct answers 71% but needs further more courses and lectures in this topic need to be implemented lab investigations importance, needs, interpretation and procedures. Which of the lab investigation is mandatory for the dentist? Availability of lab investigation in the new building of the dental hospital in king Saud University.
keywords: Awareness; Dentist; Lab test; Disease
Introduction
The purpose of the research is to survey the level of knowledge in Dentists about common diseases and their lab investigations. and to increase the awareness of dentist about common diseases and their tests and to know what is the normal value for each tests so then can know the abnormal value and detect the disease if it is not detect it.
Literature review
Blood glucose tests: [1]
a. Detect Hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia
b. Used for screening for diabetes in patients who are at risk
c. Used to monitor glucose level in patients diagnosed with diabetes
Coagulation tests: [1]
Platelet count:
a) Between 150,000 and 450,000/mm3 in healthy patients
b) No spontaneous bleeding at 10,000 to 20,000/mm3
c) Below 10,000/mm3 will require platelet transfer
d) Surgical bleeding at 50,000/mm3
Bleeding time (BT):
a. Between 1 to 6 minutes in healthy patients
b. Above 15 minutes is considered prolonged
c. Skin bleeding time is not a good indicator of other sites
Prothrombin time (PT)/international normalized ratio (INR):
a) The PT and INR are used to evaluate the extrinsic pathway
b) PT is between 11 to 13 seconds in healthy patients
c) INR is 1.0 for healthy patients
Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT):
a. Used to evaluate the intrinsic pathway of coagulation
b. Between 15 to 35 seconds in healthy patients
c. Loss of 70% of factors in common pathway lead to prolonged aPTT
Thrombin time (TT):
a) Used to test the ability to form the fibrin clot from fibrinogen
b) Between 9 to 13 seconds in healthy patients
c) Considered abnormally high when value is over 16 to 18
Kidney function tests: [2]
i. Serum Chemistry
ii. Bence jones test
iii. Creatinine Clearance Test
Thyroid function test: [3]
TSH test: It used for evaluating thyroid function
TSH high = (primary hypothyroidism)
TSH low = (hyperthyroidism)?
(T4): The free T4 fraction is the most important to determine
how the thyroid is functioning
FT4 high = hyperthyroidism [4].
FT4 low = hypothyroidism
(T3): T3 tests are often useful to diagnosis hyperthyroidism or to determine the severity of the hyperthyroidism. [5].
T3 high = hyperthyroidism
T3 testing is rarely helpful in the hypothyroid patient [6].
Cholesterol [7] is a waxy, fat-like compound that belongs to a class of molecules called steroids. It’s found in many foods, in bloodstream and in all body cells.
Hepatitis: [5]
Hepatitis B: Markers for hepatitis type B is: HBsAg; Anti-HBc; IgM anti-HBc; Anti-HBs
Material and Methods
Study design
Prospective study (survey):
Study setting: Survey give to dentists multiple choices and checklist about common diseases and their lab investigations and it will be collected and analyzed statistically.
Target population/sample size: Dentist and dental student and sample size 120 participants.
Inclusion criteria: Dentist and dental student.
Exclusion criteria: Neither non dentist nor dental student.
Ethical consideration: No need for consent form as we collected the data survey from dentist and dental student who agreed verbally and agreed to do the survey.
Data collection/data source: Survey containing multiple choice questions and checklist to know the level of knowledge of dentist and dental student it will be digital survey of sample size 120 participants was chosen from king Saud college of dentistry and other centers by e-mail and social networks 82 male and 38 female.
Statistical Analysis
The data was collected, summarized, and coded. All statistical analyses were performed with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) program (version 22). Descriptive statistic, mean, stand deviation, tables and graphs will be described. For Inferential statistics, independent t test and one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by tukey test will be used to compare the means of the groups. In the analysis p value less than 0.05 will considered significance.
Results
Figure 1:
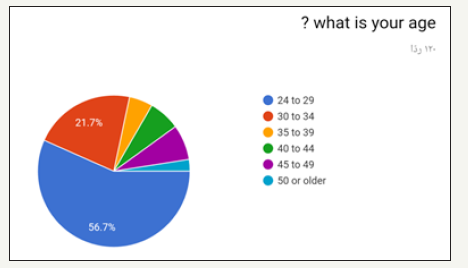
Figure 2:
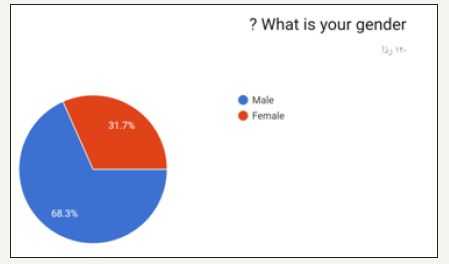
Figure 3:
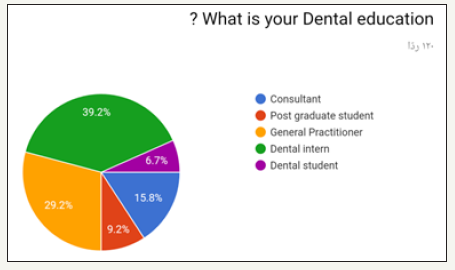
Figure 4:
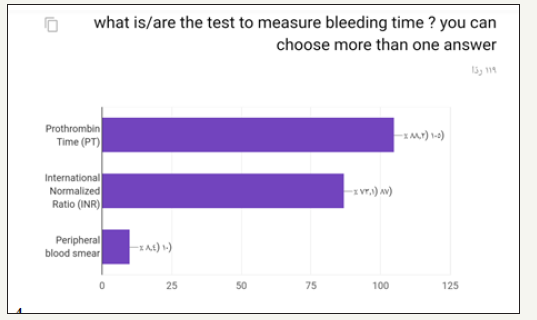
In the prospective study (survey) for dentist and dental students. Most of the participants in the survey between 24 to 29 years old as shown in (Figure 1). Most of the participant in survey are males as shown in (Figure 2). Most of the participant are dental interns and least are dental student (Figure 3). The highest test chosen was prothrombin time (PT) and least was peripheral blood smear as shown in (Figure 4). Most chosen test was glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and least was dilated eye exam as shown in (Figure 5). The highest test chosen were sphygmomanometer and Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and least was stethoscope as shown in (Figure 6). The highest platelet count chosen was 150,000 to 450,000/mm3 and least was 10,000 to 20,000/mm3 as shown in (Figure 7). The highest bleeding time chosen Between 1 to 6 minutes and the least was Between 18 to 25 minutes as shown in (Figure 8). The highest markers for HB chosen was HBs Ag, Anti-HBc, anti-HBs and least was HBs Ag, Anti-HBm, anti-HBs as shown in (Figure 9). The highest option chosen was High-density lipoproteins (HDL) and least was Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) as shown in (Figure 10). The highest tests chosen were (Serum Chemistry, Bence jones test, Creatinine Clearance Test) and least chosen were (Serum Chemistry, Bence jones test, Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time) as shown in (Figure 11).
Figure 5:
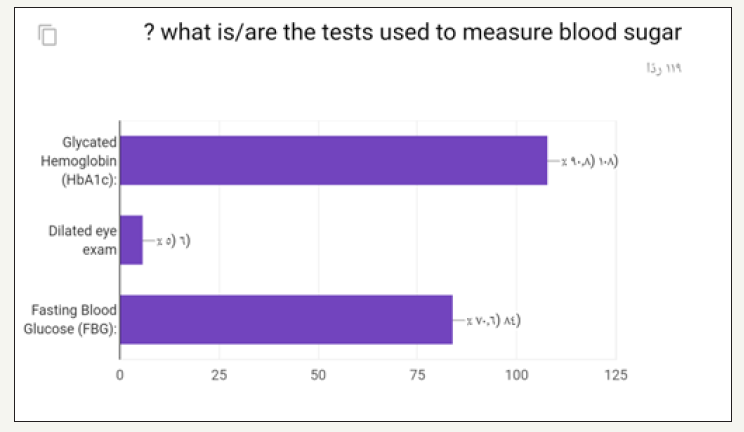
Figure 6:
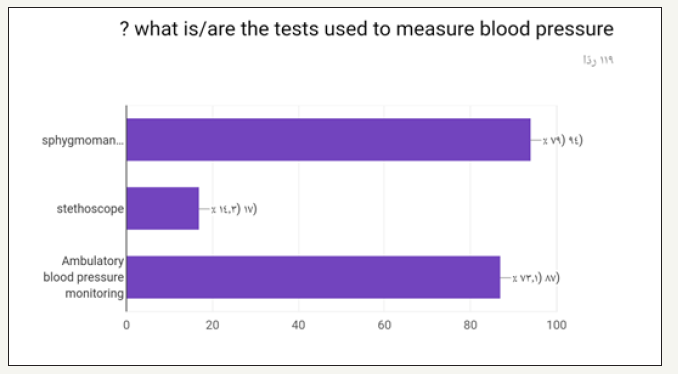
Figure 7:
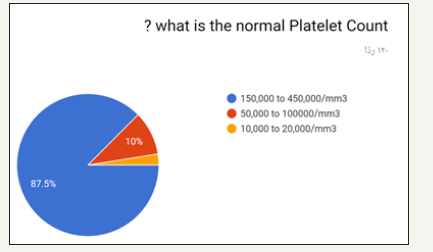
Figure 8:
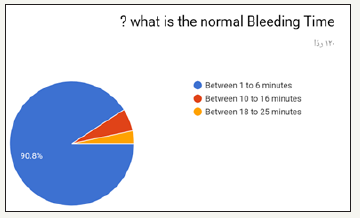
Figure 9:
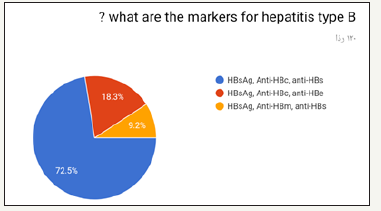
Figure 10:
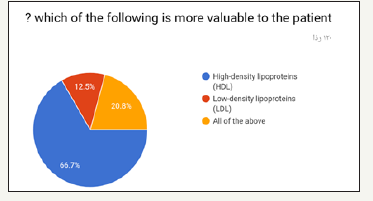
Figure 11:
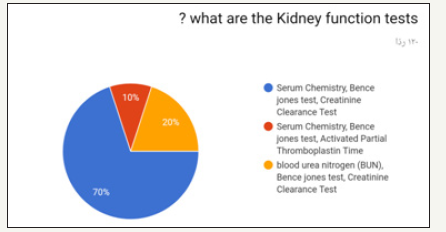
Figure 12:
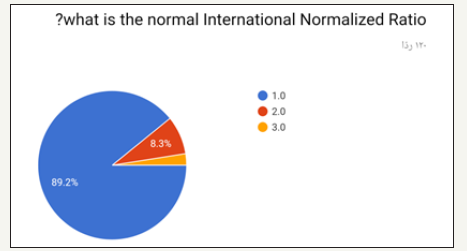
Figure 13:
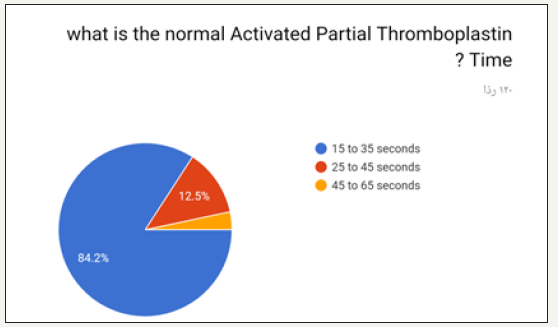
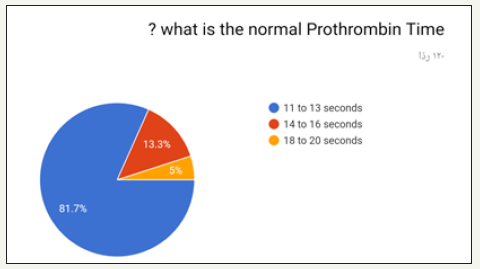
The highest option chosen was 1.0 and least was 3.0 as shown in (Figure 12). Highest option chosen was 15 to 35 seconds and least was 45 to 65 seconds as shown in (Figure 13). Highest option chosen Between 7 to 11 seconds and least was 16 to 18 seconds as shown in (Figure 14). Highest option chosen was TSH test, T4, T3 and least was Thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPO), T4, T3 as shown in (Figure 15). Highest option chosen Between 11 to 13 seconds and least was 18 to 20 seconds as shown in (Figure 16). The results of correct answers per question showed values as following:
Figure 14:
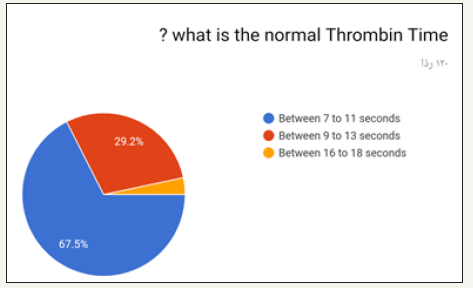
Figure 15:
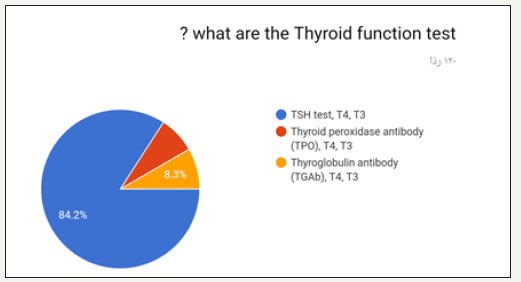
Figure 16:
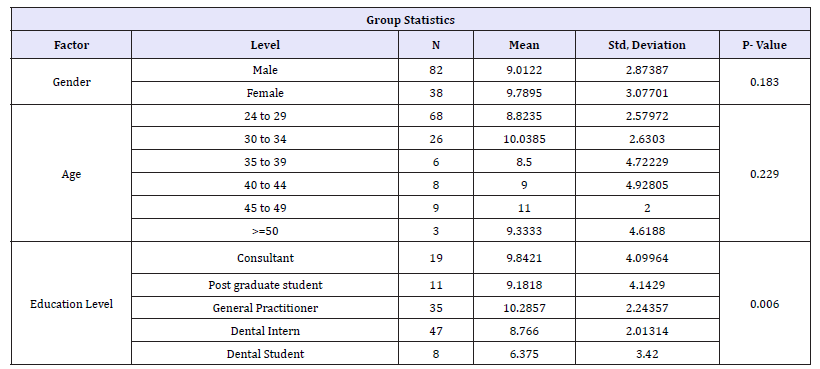
With lowest correct answer 28.9% in (Q14. what is the normal Thrombin Time?) and highest correct answer in 90.1% (Q8. what is the normal Bleeding Time?) and nearly five questions above 80% and almost average of 70% for all questions as shown in (Figure 17). Correct answers of male group with mean 9.0122±2.87387 compared to female group 9.7895±3.07701 and p value 0.183 showed no significance, and we have age groups the mean and standard deviation in (Table 1) and p values 0.229 showed no significance and, education level groups the highest mean were general practitioners 10.2857±2.24357 and consultants 9.8421±4.09964 and lowest were dental student.
Figure 17:

Table 1:
Discussion
The results showed least awareness in the answers was the answers of questions 6 and 14. (Q6. what is/are the tests used to measure blood pressure?) And correct answer was sphygmomanometer and Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and 47.1% of participants answered it correctly. (Q14. what is the normal Thrombin Time?) The correct answer was between 9 to 13 seconds and 28.9% of participants answered it correctly. In the other hands the highest awareness in the answers was the answers of questions 7,8 and 12. (Q7. what is the normal Platelet Count?) The correct answer was 150,000 to 450,000/mm3 and 86.6% of participants answered it correctly. (Q8. what is the normal Bleeding Time?) The correct answer was Between 1 to 6 minutes and 90.1% of participants answered it correctly. The education level factor in the group statistic showed the highest mean were general practitioner and consultants due to the knowledge and the experience while dental interns and dental students showed the lowest mean because the dental student lack the knowledge. According to results of Robati R & Farokhi [8] it seems vital to promote awareness level of dentists in this regard due to significance of dentistry measures in systemic patients including in bleeding disorders [9,10]. The present research was consistent with Robati R & Farokhi [8] findings because they also implied low awareness level of dentists.
Conclusion
Based on the data of this study, it can be concluded that There is knowledge toward common diseases and their lab investigations by the dentists and dental students because the average of the correct answers 71% but needs furthermore courses and lectures in these topics need to be implemented to increase the awareness of common diseases and their lab investigations importance, needs, interpretation and procedures. Which of the lab investigation is mandatory for the dentist? Availability of lab investigation in the new building of the dental hospital in King Saud University.
References
- Balaji SM (2013) Textbook of oral and maxillofacial surgery. (2nd edn), New Delhi, India.
- Collins AJ, Kasiske B, Herzog C, Chavers B, Foley R, et al. (2005) Excerpts from the United States renal data system 2004 annual data report: Atlas of end-stage renal disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 45(1 Suppl 1): A5-A7, S1-S280.
- Smallridge RC, Ain KB, Asa SL, Bible KC, Brierley JD, et al. (2012) American thyroid association guidelines for management of patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer. Thyroid 22(11): 1104-1139.
- Mary AL, Tietz NW (1995) Clinical guide to laboratory tests. (3rd edn), W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
- Ryan KJ, Ray CG (2004) Sherris medical microbiology: An introduction to infectious diseases. In: McGraw H (Ed.), (4th edn), New York, USA.
- Murray PR, Baron EJ, Pfaller MA, Tenover PC, Yolken RH (1995) Manual of clinical microbiology. (6th edn), American Society for Microbiology, Washington, USA.
- Haney EM, Huffman LH, Bougatsos C, Freeman M, Steiner RD, et al. (2007) Screening and treatment for lipid disorders in children and adolescents: systematic evidence review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Pediatrics 120(1): e189-e214.
- Robati R, Farokhi M (2013) Evaluation the dentists’ awareness of inherited bleeding disorders and anticoagulants in Shiraz. Iran J Ped Hematol Oncol 3(4): 159-163.
- Lockhart PB, Gibson J, Pond SH, Leitch J (2003) Dental management considerations for the patient with an acquired coagulopathy. Part 1: Coagulopathies from systemic disease. Brit Dent J 195(8): 439-445.
- Israels S, Schwetz N, Boyar R, McNicol A (2006) Bleeding disorders: characterization, dental considerations and management. J Can Dent Assoc 72(9): 827.
© 2018 Magdy Khaled Hamam. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)













.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)














.png)

.png)



.png)






