- Submissions

Full Text
Intervention in Obesity & Diabetes
In Vitro Radical Scavenging Activity and Modulating Effect of Annona Cherimola on Complications Associated With Diabetes in Experimental Diabetic Rats-An Approach to Evaluate Asymmetrical Temperature Distribution Analysis Using Thermography
Syed Zameer Ahmed Khader1, Sidhra Syed Zameer Ahmed1*, Nithiya Priya B Thirunavukkarasu1, Krishnaveni Radhakrishnan1, Muniraj Chinnusamy2, Venkatesan Thangavel2, Kisore P Venkatesh1, Karamchand Ravi1, Rajadurai S Ramachandran1, Moogambigai S Muthukumar1.
1 Department of Biotechnology, K S Rangasamy College of Technology, India
2 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, K S Rangasamy College of Technology, India
*Corresponding author:Dr. Sidhra Syed Zameer Ahmed, Associate Professor Youn g Scientist-SERB (DST), Department of Biotechnology, K S Rangasamy College of Technology, Tiruchengode-637215, Tamil Nadu, India
Submission: March 27, 2018;Published: June 26, 2018

ISSN 2578-0263Volume1 Issue5
Abstract
The present research explores the traditional usage of Annona cherimola and validates its usage experimentally against diabetic complication and oxidative stress. Results of proximal constituents illustrated higher ash content (89.6%) representing edible nature and contains required amount of micro and macronutrients. In vitro α amylase inhibition assay with 26-57% inhibition justifies the usage of Annona cherimola to combat diabetes, further treatment with Annona cherimola extract to alloxan induced diabetic rats showed significant activity against diabetes by regulating the release of Insulin (46-159%), C-peptide (61-72%), maintaining the levels of GHb (1-28/%) and atherogenic index. Similarly, the altered renal (urea, uric acid and creatinine) and liver markers (SGOT, SGPT and ALP) was significantly reverted back to near normal levels after treatment. Meanwhile, enzymatic antioxidant (SOD, CAT) levels demonstrated the improvement in radical scavenging potential in liver and kidney tissues of diabetic rats after treatment. An attempt is made to understand the relationship between physiological responses associated with regulation of body temperature using animal surface temperature images captured with infrared camera. Whole body asymmetrical temperature distribution analysis results revealed significant temperature change in experimental animals with 1 to 5% carried out in abdominal area and observed reduction in temperature during treatment.
Keywords: Diabetes; Antioxidant; Body temperature; Annona cherimola; Thermography
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic disorders with elevated blood glucose levels or hyperglycemia [1] and currently it is one of the most costly and burdensome chronic diseases [2]. The diabetic patient exhibits a higher risk in the development of several chronic health complications including obesity, atherosclerosis, dyslipidemia and renal failure worldwide [3]. Commercial available oral hypoglycemic drugs for diabetes mellitus produces severe side effects including hypoglycemia, weight gain, gastrointestinal disturbances and hepato-renal toxicity [4,5].
Pancreatic α-amylase and intestinal α-glucosidase plays important role during glucose metabolism, but during diabetic condition the elevation of blood glucose is also due to the action of pancreatic α-amylase and intestinal α-glucosidase. These hydrolyzing enzymes can also be an effective therapeutic method to maintain the elevated blood glucose level; hence inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase can be a key strategy in the control of diabetes mellitus [6].
As an alternative, herbal products and their derivatives act as a source of therapeutic agents in traditional medicines with a great concern to the scientific community to evaluate and isolated natural products in experimental studies. These herbal remedies are apparently effective, produce minimal or no side effects in clinical experiments and are of relatively low costs as compared to oral synthetic hypoglycaemi agents [7]. It is a well-known fact that free radicals produced in the human system causes oxidative damage by release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) from activated neutrophil and macrophages. Hence produce damages to various organs inducing diseases like diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, heart disease, arthritis, autism, cancer, Alzheimer’s dementia, cataracts and aging [8].
Annonacherimola a commonly used folk medicine against anti parasitic, antitumor, treatment of intestinal diseases, antiperoxidative and cytoprotective, etc, [9,10]. Research has proved that Annonacherimola has the capacity to scavenge free radicles and based on the above observation an effort was made to analyze its efficiency against oxidative stress produced during diabetes, combating diabetic complication.
Materials and Methods
Collection and preparation of plant material
Fresh and young leaves of Annona cherimola were collected from Nilgris district, Tamil Nadu and authenticated. The leaves were thoroughly cleaned many times with distilled water to remove dirt and contaminations, further shade dried, coarsely powdered using electric blender and stored in an air-tight container for further use and extraction [11].
Chemicals and solvents
All the chemicals, solvents were of analytical grade, purchased from Fischer Inorganic and Aromatic Limited, Chennai, India. Alloxan monohydrate was procured from SD Fine Chem. Limited, Mumbai, India.
Estimation of mineral, chlorophylls, carotenoids and alpha amylase inhibition assay
Mineral contents like phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, manganese, zinc, calcium, sulphur, copper, chromium, arsenic, nickel, aluminium, sodium, ash was determined using Atomic adsorption spectrophotometer as per the method suggested by the Association of Official Analytical Chemist [12]. Chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b and carotenoid content were analyzed using spectrophotometer method described by Arnon [13], alpha amylase inhibition assay was determined by the protocol described earlier [14,15].
Experimental induction of diabetes
Adult male Albino wistar rats weighing around 180-200g were procured from Animal House facility, K.S.R.C.T.B.T and the experiment was conducted with approval from IAEC (KSRCT/BT/ IAEC/2017/19). Diabetes was induced in overnight fasted rats with single intraperitoneal injection of alloxan monohydrate (150mg/ kg b.w.). Blood Glucose level were monitored after induction and diabetes was confirmed after 72hrs [15].
Experimental design
Rats were divided in to three groups, six rats in each group.
a) Diabetes induced rats treated with Annona cherimola (250mg/kg b.w.)
b) Diabetes induced rats treated with Annona cherimola (500mg/kg b.w.)
c) Diabetes induced rats treated with standard drug glibenclamide (10mg/kg b.w.) [16].
Animals were maintained at ambient temperature throughout the experimental period. Extracts and drug were supplemented using an intra gastric tube for 25 days and fasting blood glucose was monitored every week throughout the experiment. The animals were sacrificed by decapitation and the blood and tissue samples were collected for further investigation.
Infrared thermal imaging of animals
Infrared camera (FLIR T420, FLIR Systems, Boston, MA, USA) with wide temperature range of -4 to 2192 °F (-20 to 1700 °C), FOV 25°× 19°, and thermal sensitivity of 0.1 °C was used in this study. As a baseline anterior to posterior view of whole body, thermal images of all the rats were taken under standard conditions at constant distance of (12cm). Thermal images were taken in normal rats, alloxan induced rats, during treatment and after treatment for a period of five weeks
Biochemical profiling and antioxidant
Body weights of all the experimental animals were monitored using digital weighing scale, blood glucose using GlucoChek glucose estimation kit (Aspen diagnostic (P) Ltd. Delhi, India), Insulin was estimated using Radio immuno assay (RIA) kit supplied by Linco research Inc, Stat diagnostic, Mumbai, India. C peptide was estimated following the method of described earlier [17]. Lipid profile was estimated using standard kits purchased from Trans Asia Bio Medical Limited, Mumbai, India. Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL-C) and low density lipoprotein (LDL- C) [18]. Urea, Uric acid and creatinine were estimated using standard reagent kits purchased from Coral clinical systems, Goa, India. Alanine transaminase, alkaline phosphatise using standard kits purchased from Transasia Bio Medical Limited, Mumbai, India. SOD and catalase were assessed following the methods described earlier [19,20].
Statistical analysis
Values are presented as means±SEM. The statistical significance was evaluated by one-way using the statistical software SPSS Version 17 (Origin Lab Corporation, USA). The data were analyzed by one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s test.
Results and Discussion
Proximal composition, mineral analysis, chlorophyll and carotenoids estimation
Availability of micro and macro nutrients is represented in (Table 1). The increased percentage of ash content (89.65%) in Annona cherimola indicates that it has rich sources of mineral contents. Reports of previous research suggest that ash content in plants plays vital role in the assessment of quality of functional properties of foods [21]. Trace elements like Chromium, arsenic, manganese, zinc, aluminum, nickel, sulphur and copper were also analyzed and were found to be hardly noticeable. Meanwhile, higher amount of macronutrients like sodium, potassium, phosphorous and calcium was found in the samples. Similarly, the levels of potassium are high when compared to sodium levels giving low Na/K ratio favoring the nutritional point of view that diet with low Na/K ratio are associated with lower incidence of hypertension [22]. Hence Annona cherimola can be choice of drug in combatting diabetes.
Table 1:Analysis of micro and macro nutrients in Annona cherimola.

Table 2:Quantification of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids in Annona cherimola.
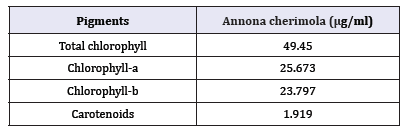
The absorbance for chlorophyll and carotenoid in Annona cherimola leaves were found at different wavelength in (Table 2). The results indicated that the amount of total chlorophyll, chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b and carotenoids present in the leaves of Annona cherimola are 49.45, 25.673, 23.797 and 1.919μg/ ml. Our results are in line with previous reports demonstrated the availability of chlorophyll content present in medicinal plant Melothiramaderaspatana [23].
Effect of Annona cherimola extract on α- amylase inhibition assay
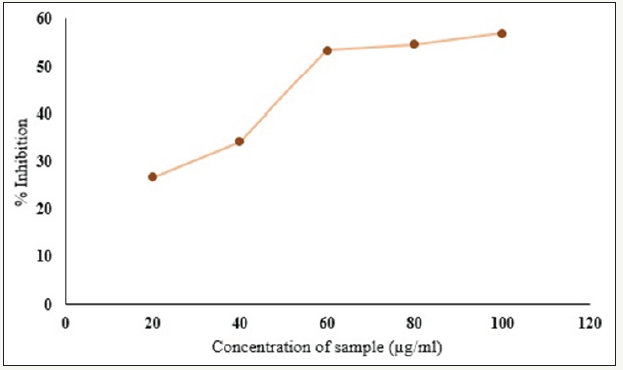
The alpha amylase inhibition assay was determined to evaluate the ability of Annona cherimola to inhibit alpha-amylase, a digestive enzyme secreted by pancreas and salivary gland. Many crude drugs inhibit alpha-amylase activity [24] and are beneficial in reducing the post prandial hyperglycemia by delaying the digestion of carbohydrates. The aqueous leaf extracts shows a powerful inhibition to alpha amylase with 26 to 57% dose dependent inhibition (Figure 1).
Figure 1:Evaluation of alpha amylase inhibition activity of aqueous leaf extract of Annona cherimola
Effect of Annona cherimola on body temperature in experimental rats
The results of the present study reveals that the circulation of blood flow in normal rats represents healthiness of the rat, whereas in alloxan induced diabetic rats the raise in body temperature is observed which might be due to increased circulation due to damaged pancreatic islets reducing the impact of damage caused by alloxan (Figure 2). Similarly, the thermal images of drug treated and Annona cherimola treated groups observed gradual fall in temperature throughout the experimental period, representing the efficiency of Annona cherimola diminishing the diabetic complication and improving blood circulation with 1 to 5% asymmetric abdominal temperature changes (Figure 3 & 4) illustrates the observation recorded using FLIR camera at two different abdominal sites of experimental rats and representing the temperature changes.
Figure 2:Effect of Annona cherimola on body temperature in experimental rats.
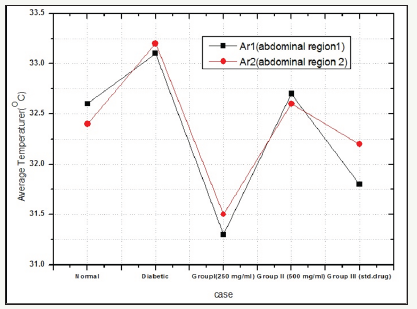
Figure 3:Effect of Annona cherimolaon asymmetric temperature in experimental rats.
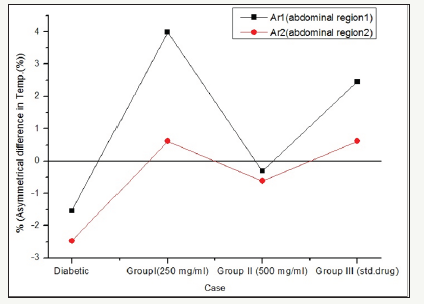
Figure 4:Thermal imaging of diabetic rats representing thermo gram of normal rat, Group I, Group II, Group III.
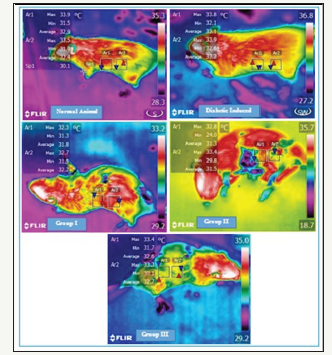
Skin plays a predominant role in maintaining and regulating body temperature [25] and any specific damage in the system can be examined by thermography technology and studies have reported diabetic foot lesions and ulceration can be easily detected before complications using a thermography [26,27]. An attempt is made to identify the temperature changes during diabetic condition representing raise in temperature during diabetic condition and gradual reduction in temperature after treatment.
Effect of Annona cherimola extracts on body weight, blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, C-peptide and insulin
Decrease in body weight, insulin and C- Peptide is a common phenomenon observed in the experimental diabetes [28] and was also observed in the present study (Table 3). Research has proved that diabetes induction causes significant alteration because of increase muscle wasting, loss of tissue protein and abnormal secretion of the hormone due to pancreatic β‐cells damage there by inhibiting insulin release [11]. Similar effect was observed in the present study, but treatment with Annona cherimola has pronounced effect in improving the body weight (21-29%) and has reverted the changes in glucose (28-51%), insulin (46-159%), GHb (1-28/%) and C peptide (61-72%) in all the groups when compared with regular intervals and the values are on par with the drug treated groups. The present finding is in line with the previous findings of other medicinal plants demonstrating anti diabetic activity [28,29].
Table 3:Effect of Annona cherimola on body weight, blood glucose, glycosylated haemoglobin and insulin in experimental rats.
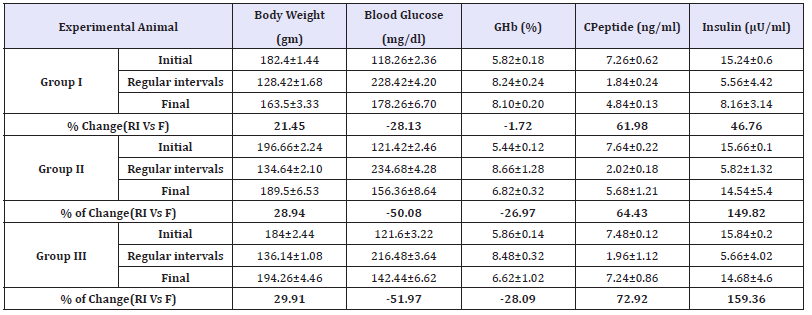
All the value represents six individual observations, and the data are expressed in mean±SEM calculated by one- way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. Initial: Before alloxan induction, Regular intervals-Analysis carried out weekly once after induction, Final observation -end of the experiment.
±indicates the percentage of change during and after the treatment
Effect of Annona cherimola extracts on Lipid profile
It is a well-known fact that cardiovascular complications such as atherogenesis, fatty liver and coronary artery disease are the factors associated with diabetes mellitus due to the abnormal lipid metabolism. The altered levels in lipid profile (before and after induction) can be observed in (Table 4). In Annona cherimola treated groups animals elevated levels of TC, LDL-C, VLDL and TG were significantly reduced by27 & 51%, 127 &213%, 43 & 72%, 54 &87%respectively on comparing with the values during regular intervals. Similarly, decreased HDL levels was gained back to near normal levels with an increase by 26 & 39% (Table 4). These results are on par with the drug treated groups and are in line with the previous studies with other plants demonstrating antihyperglycemic and hypolipidimic activity, lowering atherogenic index [14].
Table 4:Effect of Annona cherimola on lipid profile in experimental rats.
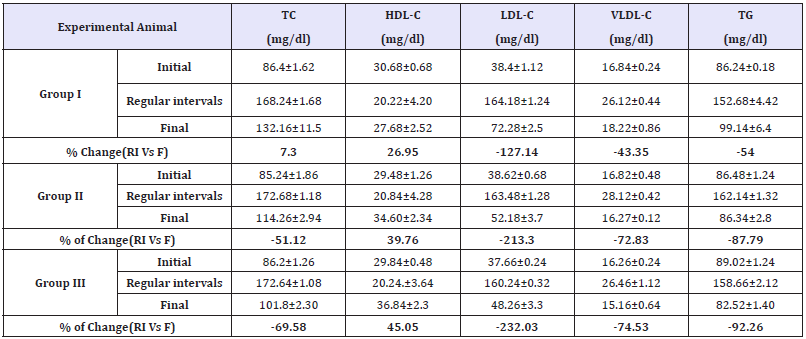
All the value represents six individual observations, and the data are expressed in mean±SEM calculated by one- way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. Initial: Before alloxan induction, Regular intervals-Analysis carried out weekly once after induction, Final observation -end of the experiment.
±indicates the percentage of change during and after the treatment.
Effect of Annona cherimola extracts on liver and renal markers
The effect of Annona cherimola extract on liver and renal markers in experimental diabetes is represented in (Table 5). Liver plays a main role in monitoring insulin clearance, maintaining postprandial glucose levels and it is evident that amino transferases is one of the markers of the healthy hepatocytes [30] and any alteration in liver function is observed with increasing in SGOT & SGPT levels after alloxan induction [31] due to the destruction of liver cells causing release of these enzymes in cytosol into the blood stream [32]. Similarly increase in SGOT and SGPT is observed in initial observation with regular intervals. Treatment of diabetic rats with aqueous leaf extract of Annona cherimola with concentration 250 and 500mg/kg b.w caused a reduction in the activity of these enzymes by SGOT by 41 & 50%; SGPT 14 & 37%; ALP 35 & 53% respectively (Table 5).
Table 5:Effect of Annona cherimola on lipid profile in experimental rats.
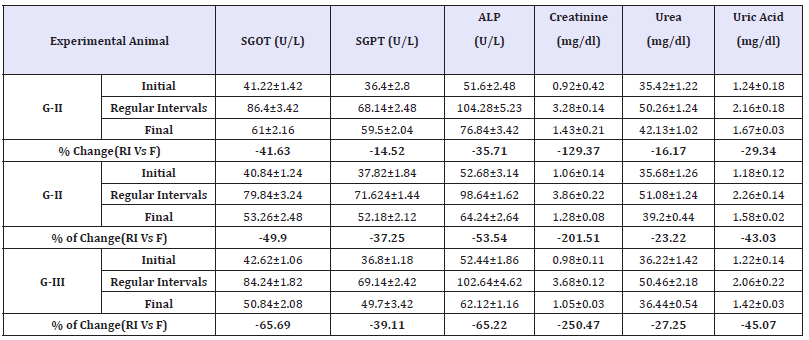
All the value represents six individual observations, and the data are expressed in mean±SEM calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. Initial: Before alloxan induction, Regular intervals-Analysis carried out weekly once after induction, Final observation - end of the experiment.
±indicates the percentage of change during and after the treatment.
Diabetic associated complication includes hyper urea, hyper triglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia and creatinuria due to extensive muscle breakdown [33]. The values of creatinine, uric acid and urea was found to increase in alloxan induced diabetic rats, but after treatment there was a gradual fall in all the markers at both the concentration. Creatinine levels were reduced to 121 & 201%, urea by 16 & 23% and uric acid by 29 & 43% in Group I &II animals when compared during regular intervals. The results are in agreement with the other studies [29] demonstrating similar effect in alloxan induced experimental rats. The results of LFT and KFT are on par with the standard drug treated groups.
Effect of Annona cherimola extracts tissue antioxidant enzymes
SOD is an important defense enzyme that catalysis the dismutation of superoxide radicals. Enzyme catalysis is the hemoprotein that catalyses the decline of hydrogen peroxide and defends the tissues from the effect of hydroxyl radicals [34]. The predominant raise in liver SOD and CAT after treatment with Annona cherimola (250 and 500mg/kg b.w) indicates its beneficial action. The results of antioxidant in diabetic treated are as similar to the action with standard drug glibenclamide (10mg/kg b.w) (Table 6). Similar results were observed in previous reports of antidiabetic effect of Dilleniaindica L. leaves in diabetic rats [35].
Table 6:Effect of Annona cherimola on lipid profile in experimental rats.
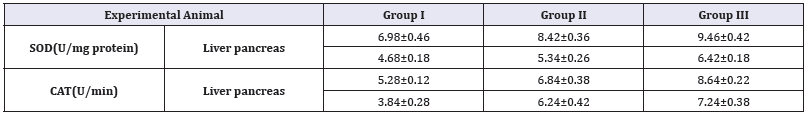
All the value represents six individual observations, and the data are expressed in mean±SEM calculated by one- way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test.
SOD: Superoxide Dismutase; CAT: Catalase
Conclusion
In the present study an attempt is being made to identify the effect of Annona cherimola over complication associated with diabetes by improving radical scavenging ability in diabetic rats. Relationship between body temperature during metabolic changes in diabetic condition was analyzed and the results reveled that imaging process can also be used to identify the abnormalities and can be a valuable tool for diagnosis.
Acknowledgement
Authors are thankful to the Management and Principal of K.S. Rangasamy College of Technology, Tiruchengode for providing infrastructure and facilities to carry out this research work successfully.
© 2018 Sidhra Syed Zameer Ahmed. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)






























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)













.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)














.png)

.png)



.png)






