- Submissions

Full Text
Forensic Science & Addiction Research
Influence of Aerobic Training on Muscular Endurance of College Hostel Students
Javaid Ahmad Sheikh1*, Zahoor Ahmad Bhat1 and M Kalimuthu1
1Department of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, Annamalai University, India
*Corresponding author: Javaid Ahmad Sheikh, Department of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, Annamalai University, Tamil Nadu, India
Submission: September 8, 2017 Published: September 22, 2017

ISSN: 2578-0042 Volume1 Issue1
Abstract
The present study was to determine the influence of aerobic training on muscular endurance of college male hostel students. Twenty male students (n=20) were randomly selected as subjects and the age were ranged between 18 and 24 years. The selected subjects were randomly assigned into two equal groups such as training group (TG) and the control group (CG) for the strengths of ten (n=10) each. Experimental training group underwent respective aerobic training programme for twelve weeks for three days per week and a session on each day. The control group did not involve in any special training apart from their regular activities. Muscular endurance was taken as criterion variable for the present and it was measured by sit ups. Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to analyse the collected data. The results revealed that that the aerobic training made significant improvement (p≤0.05) in muscular endurance of the selected subjects. The level of confidence was fixed at 0.05 in all cases.
Keywords: Aerobic training; Muscular endurance; College male hostel students
Introduction
Aerobic means in the presence oxygen. Aerobic exercise is the type of moderate-intensity physical activity that you can sustain for more than just a few minutes with the objective of improving your cardio respiratory fitness and your health. The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) defines aerobic exercises as “any activity that uses large muscle groups which can be maintained continuously, and is rhythmic in nature. The effect of aerobic training is the key to understand the basis for physical performance of athletic competition. Aerobic exercise is any physical activity that makes you sweat, causes you to breathe harder, and gets your heart beating faster than at rest. It strengthens your heart and lungs and trains your cardiovascular system to manage and deliver oxygen more quickly and efficiently throughout your body. During the early part of exercise one’s body is used to stored carbohydrates and circulating fatty acids for energy [1]. Exercise means excessive use of body muscles for a specific time regularly. Regular aerobics improves weight control, heart and lung function, blood supply, to the muscles and tissues, increased threshold [2].
Muscular endurance is the ability of a muscle to lift weight repeatedly over time. Muscular endurance is how many times you can do a full squat, a sit up, or how many times you can do a bicep curl with a light-to-moderate weight before breaking form. The ability of a muscle or muscle group is to exert force repeatedly or to sustain a contraction over a period of time [3]. Muscular endurance is the capacity of a skeletal muscle or group of muscles to continue contracting over a long period. It is the muscles ability to contract and relax repeatedly. This is usually measured by the number of times i.e. repetition, which a body can perform in given time period [4].
Materials and Methods
The present study was to determine the influence of aerobic training on muscular endurance of college male hostel students. Twenty male students (n=20) were randomly selected as subjects from Department of Physical Education, Annamalia University. The age was ranged between 18 and 24 years. The selected subjects were randomly assigned into two equal groups such as training group (TG) and the control group (CG) for the strengths of ten (n=10) each. Experimental training group underwent respective aerobic training programme for twelve weeks for three days per week and a session on each day. The control group did not involve in any special training apart from their regular activities. Muscular endurance was taken as a criterion variable and it was measured by sit ups. The experimentation was subjected to twelve weeks of aerobics training. The training programme was scheduled for one session per day between 6am to 7am. In training session the first 30 minutes of continuous running and the remaining 30 minutes of calisthenics exercises and abdominal crunches. Training was given under the direct supervision of the investigator. The progression of load was followed during experimentation, and the exercises were arranged from simple to complex.
Data Analysis
For statistical analysis Mean, Standard Deviation and Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) were used for the analysis of data, and statistical significance was fixed at 0.05 levels
Results and Discussion
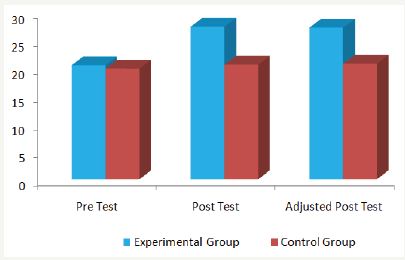
Table 1 shows that the pre test means of aerobic training group and the control group are 20.50 and 19.90 respectively. The obtained F ratio of 0.91 for the pre test mean is less than the table value 4.41 for df 1 and 18 required for significance at 0.05 level. The post test mean of aerobic training and control groups are 27.40 and 20.60 respectively. The obtained F ratio of 45.83 for post test mean is higher than the table value 4.41 for df 1 and 18 required for significance at 0.05 level. The adjusted post test mean of aerobic training group and the control group are 27.24 and 20.75 respectively. The obtained F ratio of 41.97 for adjusted post test mean is higher than the required table value 4.45 for df 1 and 17 required for significance at 0.05 level. The result of the study indicated that there was a significant difference between the adjusted post test mean of the aerobics training and the control group on muscular endurance at 0.05 levels. The pre, post and adjusted post test mean values of the aerobics training and the control group on muscular endurance is graphically represented in Figure 1.
Table 1: Analysis of covariance on muscular endurance of aerobic training group and the control group.
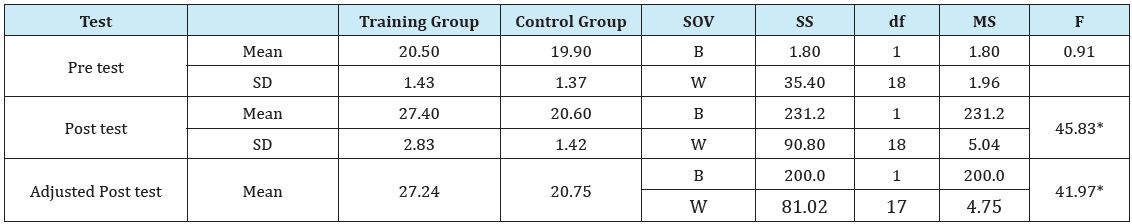
*Significant at 0.5 level of confidence
(The table value required for significance at 0.05 level of confidence with df 1 and 18 and 1 and 17 are 4.41 and 4.45 respectively)
Figure 1:: The pre, post and adjusted post test mean values of experimental group and control group on muscular endurance.
The result of the present study pointed out that there was a significant difference in a muscular endurance due to twelve weeks of aerobic training on college male hostel students. Muller [5] also conducted the same study that aerobic training improves muscle strength. Jones [6] was conducted same study that aerobic training improves exercise tolerance and ultimately improves the performance of young athletes. Fatima [7] also reached the conclusion of positive improvement in muscle endurance among the college hostel students after the systematic practice of aerobic training.
Conclusion
The result of the present study revealed that the training group has significant improvement in muscular endurance among college hostel students after the systematic aerobic training programme. It was also concluded that the aerobic training is one of the best training methods for improving the muscular endurance as well as physical fitness for young men.
References
- Dick Frank W, Carl Johnson, Wilf Paish (2006) Strength training for athletes. London brutish amateur athletic board.
- Diva Fitness (1999) Fitness -references guide to aerobics exercises, physical activity and health. A Report of the Surgeon General, p. 47.
- Robert V Hockey (1989) Physical fitness: The path way to healthful living. (6thedn), St. Louis, USA.
- Charles B Corbin, Ruth Lindsey (1994) Concepts of physical fitness with laboratories. WCB, Brown & Benchmark publishers, Indiana, USA, p. 116.
- Muller EA (1959) Traning muscles strength. Ergonomics 2(2): 216-222.
- Baxter Jones A, Goldstein H, Helms PG (1993) The development of aerobic power in young athletes. J APPL Physiol 75(3): 1160-1167.
- Syeda SF, Rehman R, Saifullah, Khan Y (2013) Physical activity and its effect on forced expiratory volume. J Pak Med Assoc 63(3): 310-312.
© 2017 Javaid Ahmad Sheikh, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
 a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in
a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Based on a work at www.crimsonpublishers.com.
Best viewed in 







.jpg)





























 Editorial Board Registrations
Editorial Board Registrations Submit your Article
Submit your Article Refer a Friend
Refer a Friend Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us
.jpg)






.jpg)













.bmp)
.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)














.png)

.png)



.png)






